Doose, C., Oger, C., Mas-Normand, L., Durand, T., Hubas, C. (2024). Non-enzymatic oxylipin production in a mudfl at microphytobenthic biofilm : evidence of a diatom response to light. Front. Photobiol. 2:1441713. doi: 10.3389/fphbi.2024.1441713
Microphytobenthos (MPB) are a diatom-dominated microbial community of primary producers that inhabit mudflat sediments. MPB contribute significantly to the total primary production of the oceans, serving as a major food source for invertebrates, fish, and wading birds, and playing a crucial role in local socioeconomic activities and the global carbon cycle. Benthic diatoms exhibit photo-protective strategies to cope with extreme light variations, which can induce cellular oxidative stress. This stress results in the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) that, in turn, generate oxylipins—oxygenated metabolites of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs)—which are known chemical mediators in diatoms. However, non-enzymatically generated oxylipins, such as isoprostanoids and isofuranoids, are not well-studied in diatoms.
To better understand the role of these compounds in the light response of migrational MPB, we investigated how different irradiances from low light to high light affect isoprostanoid production in the biofilm’s organisms. Our results showed that the PUFA precursors of varying oxylipins reflected a diatom response to irradiance. Under 1000 PAR, the total amount of isoprostanoids increased, indicating an oxidative stress response. High light conditions were characterized by the presence of isoprostanes (IsoPs) and prostaglandins (PGs), which were associated with lipid peroxidation, likely linked to elevated ROS generation from photosynthesis. In contrast, low light and medium light conditions were characterized by phytoprostanes (PhytoPs), suggesting that ROS scavengers were likely not overwhelmed in these conditions.
This initial investigation of non-enzymatic oxylipin production by a microphytobenthic biofilm under various irradiances highlights the potential for exploring their possible signaling roles in MPB light responses.
BOREA contact: Cédric Hubas, cedric.hubas@mnhn.fr
Picture titles:
- Fig. Mdf-Biofilm3 : Mécanisme de production possibles des oxylipines dont les isoprostanoides dans les biofilms de vasière/ Possible mechanisms of oxylipins, including the isoprostanoids,production in mudflat biofilms. © Doose 2024
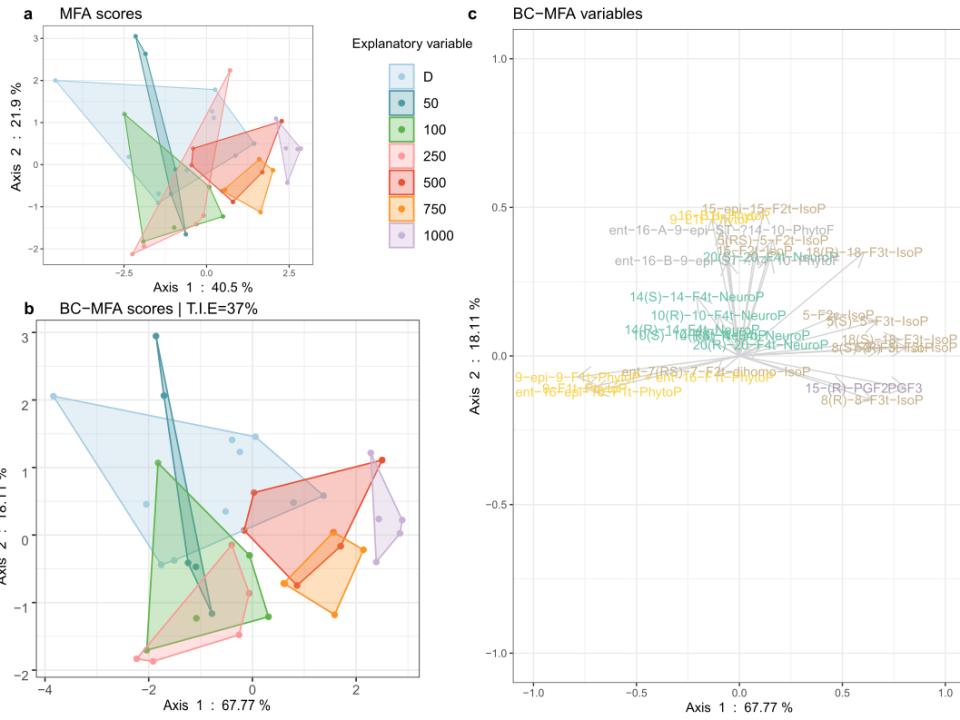
- Fig. 1 : Analyse entre classes (BC) réalisée à partir d'une analyse factorielle multiple (MFA) (A). Objet de la MFA (B). BC-MFA et ses variables (C). sur les oxylipines mesurées dans le biofilm exposé à l'obscurité (D, n = 10) et à des irradiations de faibles (LL : 50, 100), moyenne (ML : 250), et fortes lumière (HL : 500, 750, 1000) en µmol. photons.m-2.s-1 PAR (n = 5). / Between-class (BC) analysis realized on a multiple factor analysis (A). MFA object (B). BC-MFA and its variables (C). on oxylipins measured in the biofilm exposed to dark (D, n = 10) and to irradiances of low (LL: 50, 100), medium (ML: 250), and high light (HL: 500, 750, 1000) in µmol. photons.m−2.s−1 PAR (n = 5). © Doose et al., 2024
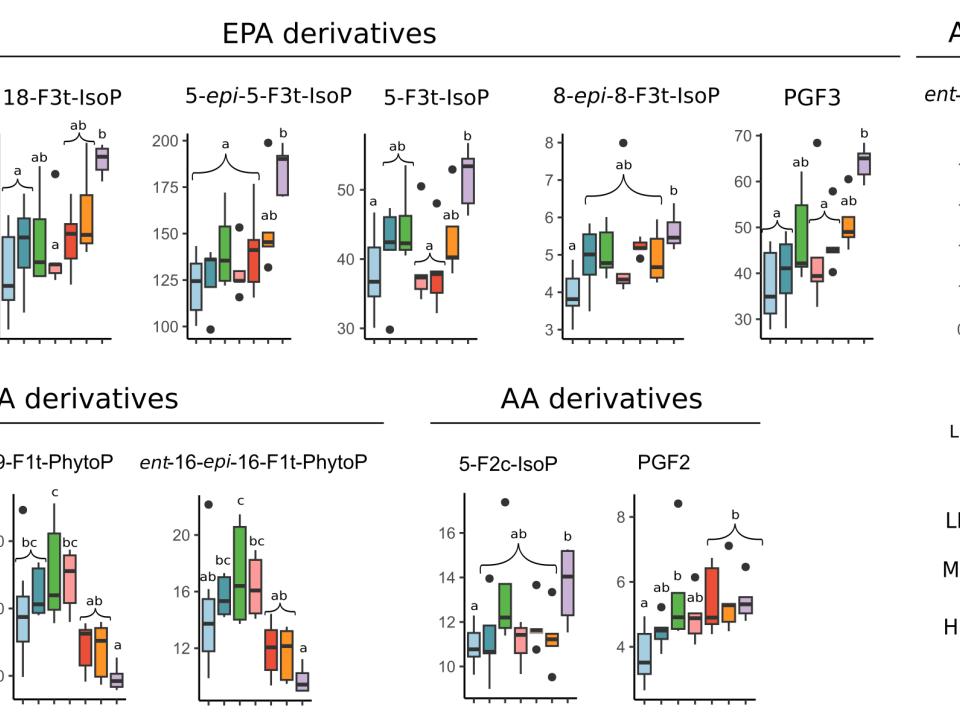
- Fig. 4 : Concentration des oxylipines en pg/mg dw variant significativement dans le biofilm exposé à l'obscurité (D, n = 10) et à des irradiations faibles (LL : 50 et 100), moyennes (ML : 250), et élevées (HL : 500, 750, et 1000) en µmol µmol. photons.m-2.s-1 PAR. Les différences significatives entre les traitements sont indiquées par des lettres (ANOVA, p < 0,05 ; n = 5). Les oxylipines ont été rassemblées en groupes correspondant à leurs acides gras précurseurs AA (acide arachidonique), AdA (acide adrénique), ALA (acide α-linolénique), DHA (acide docosahexaénoïque) et EPA (acide eicosapentaénoïque). / Concentration of oxylipins in pg/mg dw which significantly varied in biofilm exposed to dark (D, n = 10) and to irradiances of low (LL: 50 and 100), medium (ML: 250), and high light (HL: 500, 750, and 1000) in µmol µmol. photons.m-2.s-1 PAR. One-way ANOVA was performed on the data to detect significant differences between treatments, as indicated by letters (p < 0.05; n = 5). Oxylipins were gathered in groups corresponding to their fatty acid precursors AA (arachidonic acid), AdA (adrenic acid), ALA (α-linolenic acid), DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), and EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid). © Doose et al., 2024.
To better understand the role of these compounds in the light response of migrational MPB, we investigated how different irradiances from low light to high light affect isoprostanoid production in the biofilm’s organisms. Our results showed that the PUFA precursors of varying oxylipins reflected a diatom response to irradiance. Under 1000 PAR, the total amount of isoprostanoids increased, indicating an oxidative stress response. High light conditions were characterized by the presence of isoprostanes (IsoPs) and prostaglandins (PGs), which were associated with lipid peroxidation, likely linked to elevated ROS generation from photosynthesis. In contrast, low light and medium light conditions were characterized by phytoprostanes (PhytoPs), suggesting that ROS scavengers were likely not overwhelmed in these conditions.
This initial investigation of non-enzymatic oxylipin production by a microphytobenthic biofilm under various irradiances highlights the potential for exploring their possible signaling roles in MPB light responses.
BOREA contact: Cédric Hubas, cedric.hubas@mnhn.fr
Picture titles:
- Fig. Mdf-Biofilm3 : Mécanisme de production possibles des oxylipines dont les isoprostanoides dans les biofilms de vasière/ Possible mechanisms of oxylipins, including the isoprostanoids,production in mudflat biofilms. © Doose 2024
- Fig. 1 : Analyse entre classes (BC) réalisée à partir d'une analyse factorielle multiple (MFA) (A). Objet de la MFA (B). BC-MFA et ses variables (C). sur les oxylipines mesurées dans le biofilm exposé à l'obscurité (D, n = 10) et à des irradiations de faibles (LL : 50, 100), moyenne (ML : 250), et fortes lumière (HL : 500, 750, 1000) en µmol. photons.m-2.s-1 PAR (n = 5). / Between-class (BC) analysis realized on a multiple factor analysis (A). MFA object (B). BC-MFA and its variables (C). on oxylipins measured in the biofilm exposed to dark (D, n = 10) and to irradiances of low (LL: 50, 100), medium (ML: 250), and high light (HL: 500, 750, 1000) in µmol. photons.m−2.s−1 PAR (n = 5). © Doose et al., 2024
- Fig. 4 : Concentration des oxylipines en pg/mg dw variant significativement dans le biofilm exposé à l'obscurité (D, n = 10) et à des irradiations faibles (LL : 50 et 100), moyennes (ML : 250), et élevées (HL : 500, 750, et 1000) en µmol µmol. photons.m-2.s-1 PAR. Les différences significatives entre les traitements sont indiquées par des lettres (ANOVA, p < 0,05 ; n = 5). Les oxylipines ont été rassemblées en groupes correspondant à leurs acides gras précurseurs AA (acide arachidonique), AdA (acide adrénique), ALA (acide α-linolénique), DHA (acide docosahexaénoïque) et EPA (acide eicosapentaénoïque). / Concentration of oxylipins in pg/mg dw which significantly varied in biofilm exposed to dark (D, n = 10) and to irradiances of low (LL: 50 and 100), medium (ML: 250), and high light (HL: 500, 750, and 1000) in µmol µmol. photons.m-2.s-1 PAR. One-way ANOVA was performed on the data to detect significant differences between treatments, as indicated by letters (p < 0.05; n = 5). Oxylipins were gathered in groups corresponding to their fatty acid precursors AA (arachidonic acid), AdA (adrenic acid), ALA (α-linolenic acid), DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), and EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid). © Doose et al., 2024.